

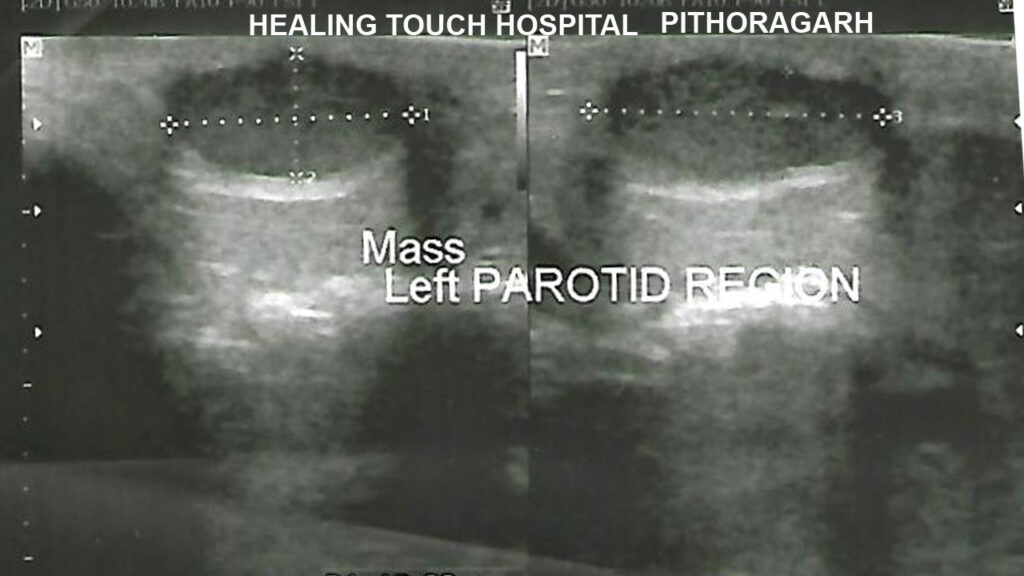
Epidermoid cyst left parotid region.
These are the most common cutaneous cysts. They may occur anywhere on the body,
face, trunk, neck, extremities, and scalp. Rarely they have been reported in bone, breast, and various intracranial locations.
Various terms have been used to describe epidermoid cysts, including follicular infundibular cysts, epidermal cysts, and epidermal inclusion cysts and sometimes as sebaceous cyst. The term milia refers to very small, superficial epidermoid cysts.
Nature of epidermoid cysts is benign; very rarely they may be associated with malignancies.
They are approximately twice as common in men than in women.
Epidermoid cysts may occur at any age; however, most commonly seen in the third and fourth decades. Milia are common in the neonatal period.
Epidermoid cysts are usually symptomless. A foul-smelling discharge of “cheeselike” material is common presentation . Less frequently, the cysts can become inflamed or infected, causing pain and tenderness.
They appear like firm, round nodules of variable size with a central pore or punctum.
Asymptomatic epidermoid cysts may not be treated.
If infected, may cause abscess in tissues and require drainage. Surgical excision is required if symptomatic or for cosmetic purposes.

Office Attendant
HRD
HEALING TOUCH HOSPITAL
BHATKOT,
PITHORAGARH, UTTARAKHAND.
PIN 262501.
e-mail : h_t_healthcare@yahoo.com
9837529400 (Hindi)
8937865314 (English)
Please check notice above.
Healing Touch Hospital, Pithoragarh is committed to take care of your health.