

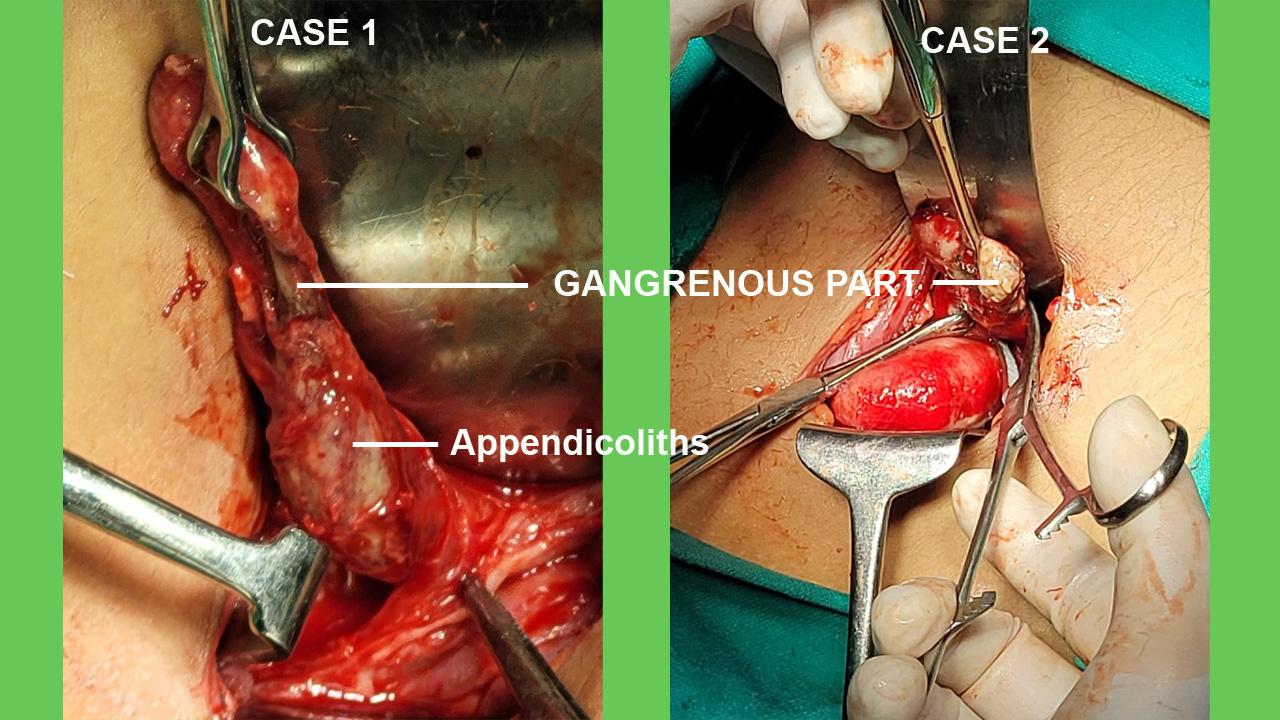
Appendicitis is defined as an inflammation of vermiform appendix.
Appendicitis remains a clinical emergency and is one of the common causes of acute abdominal pain.
One can get appendicitis at any age, but it usually affects people aged between 10 and 30 years and can affect any sex, more common in males.
Signs and symptoms:
Abdominal pain is the most common symptom, typically begins as periumbilical or epigastric region then migrates to right lower abdomen.
Nausea. Loss of appetite, vomiting usually follows. Some individuals may have
Diarrhea or constipation.
Lab tests:
CBC, C-reactive protein (CRP), Liver and pancreatic function tests
Urinalysis (for differentiating appendicitis from urinary tract conditions)
Urinary beta-hCG (for differentiating appendicitis from early ectopic pregnancy in women of childbearing age)
Urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA)
Ultrasonography
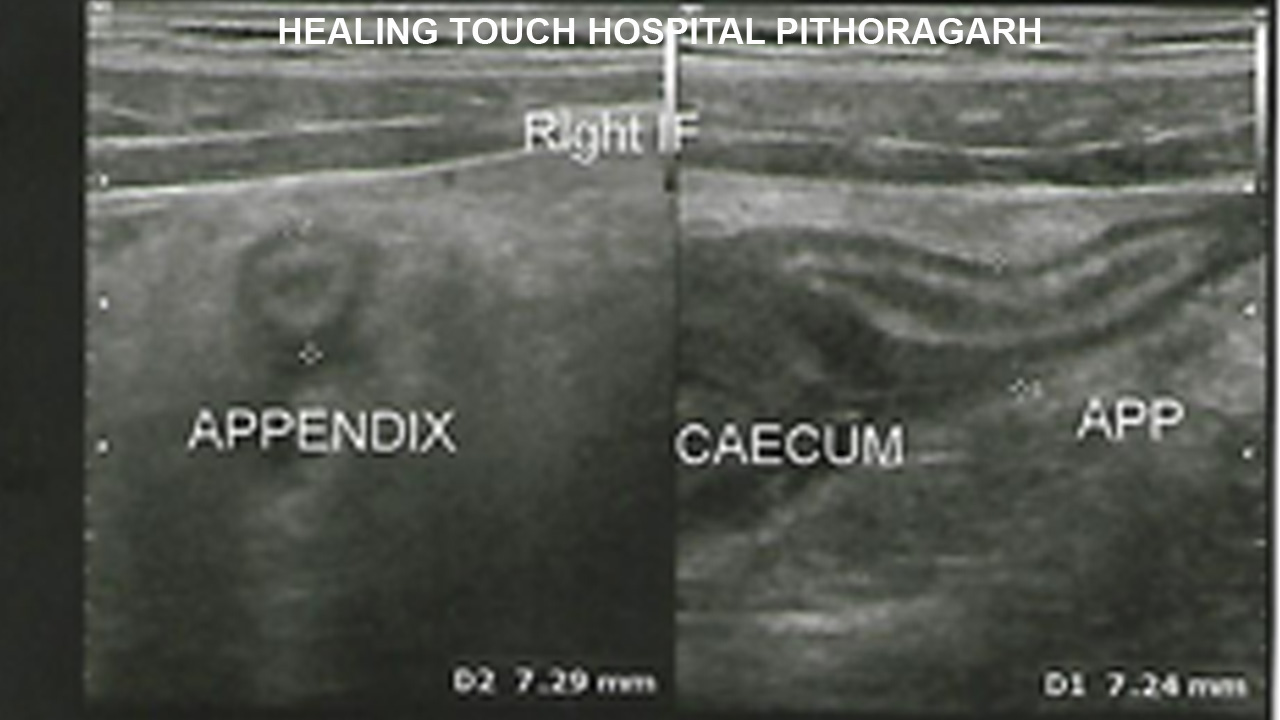
CT scan
Other imaging studies may be performed if indicated
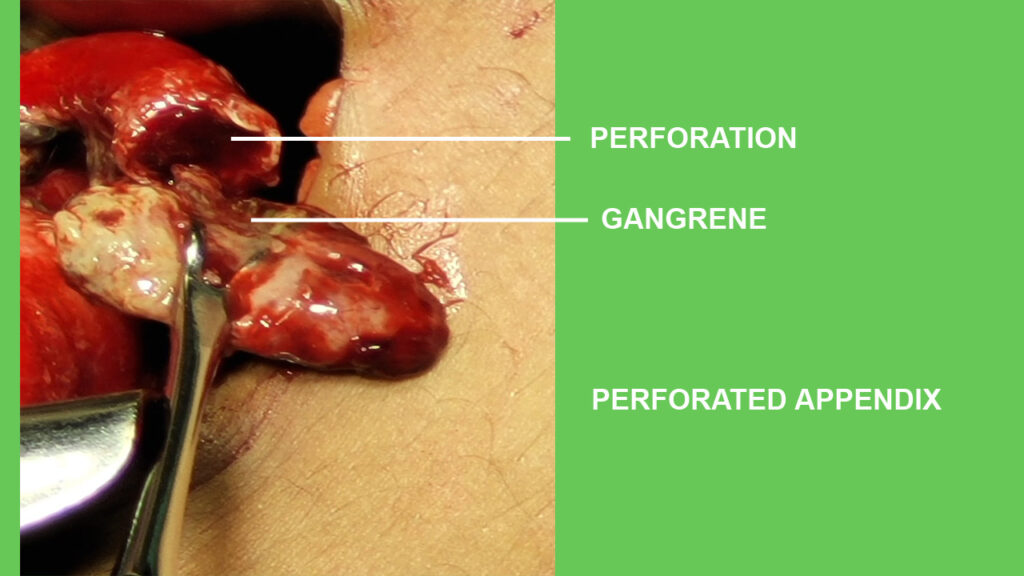
In emergency department IV fluids, antibiotics, analgesics are started.
Appendectomy remains the only curative treatment of appendicitis,
although nonoperative management is increasingly recognized as being safe and effective for uncomplicated cases of acute appendicitis.

Office Attendant
HRD
HEALING TOUCH HOSPITAL
BHATKOT,
PITHORAGARH, UTTARAKHAND.
PIN 262501.
e-mail : h_t_healthcare@yahoo.com
9837529400 (Hindi)
8937865314 (English)
Please check notice above.
Healing Touch Hospital, Pithoragarh is committed to take care of your health.